









RGBCam — free version of SpectraCam

Descrição de RGBCam — free version of SpectraCam
Our vision has high resolution and a huge dynamic range, but it mixes and poorly distinguishes spectral components. With the RGBCam app and the camera of your smartphone, find out how we look - our teeth, light-cured fillings, skin, veins and moles in the near infrared and in the near ultraviolet. How insects see flowering plants and see the world. What is the difference between cheese from milk and cheese with the addition of vegetable dyes? How are look banknotes, flowers, camouflage in narrow spectral ranges?
Features:
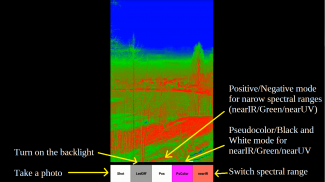
Multi-spectral photo. Take photos at once in three spectral ranges (near infrared, green, near ultraviolet), plus a normal color image.
Multispectral Viewer. View the selected part of the spectrum in real time. Green - the center of the visible spectrum, near infrared, near UV and the usual color image.
Vein viewer. * Use the LedOn / LedOff button to turn on the backlight, set the infrared spectral range (“nearIR” button) and observe the near-surface blood vessels.
Permissions:
Camera. Required for taking photos.
Storage. Required to save photo.
*: The Vein viewer does not work at all if the veins are hidden by a layer of subcutaneous fat. Usualy, for most people up to 20 years it is insignificant, and the veins are clearly visible in the infrared range on the arms, legs, head. On the neck arteries can also be seen. At age after 40 years, visibility is keep on the biceps, fist and forearm. Fist veins are visible in almost all.
In addition, the hemoglobin level matters, the higher it is, the more contrast the image. Its level depends on gender (higher for men), fitness (endurance sports), degree of fatigue, smoking. An abstract ideal variant is a man of 20-30 years old, who was engaged in cross-country skiing, with a small smoking history.
Nossa visão tem alta resolução e uma enorme faixa dinâmica, mas mistura e dificilmente distingue os componentes espectrais. Com o aplicativo RGBCam e a câmera do seu smartphone, descubra como nos parecemos - nossos dentes, preenchimentos fotopolimerizados, pele, veias e manchas no infravermelho próximo e no ultravioleta próximo. Como os insetos veem as plantas com flores e vêem o mundo. Qual é a diferença entre queijo de leite e queijo com a adição de corantes vegetais? Como estão as notas de banco, flores, camuflagem em faixas espectrais estreitas?
Funcionalidades:
Foto multi-espectral. Tire fotos de uma vez em três faixas espectrais (próximo a infravermelho, verde, próximo a ultravioleta), além de uma imagem colorida normal.
Visualizador Multiespectral. Veja a parte selecionada do espectro em tempo real. Verde - o centro do espectro visível, próximo ao infravermelho, próximo ao ultravioleta e a imagem colorida usual.
Visualizador de veias. * Use o botão LedOn / LedOff para ligar a luz de fundo, definir a faixa espectral de infravermelho (botão “nearIR”) e observar os vasos sanguíneos próximos da superfície.
Permissões:
Câmera. Necessário para tirar fotos.
Armazenamento. Necessário para salvar foto.
*: O visualizador Vein não funciona de forma alguma se as veias estiverem escondidas por uma camada de gordura subcutânea. Normalmente, para a maioria das pessoas até aos 20 anos é insignificante, e as veias são claramente visíveis na gama de infravermelhos nos braços, pernas, cabeça. Nas artérias do pescoço também pode ser visto. Na idade após os 40 anos, a visibilidade é manter-se no bíceps, punho e antebraço. Veias do punho são visíveis em quase todos.
Além disso, o nível de hemoglobina é importante, quanto mais alto, mais contraste a imagem. Seu nível depende do gênero (maior para os homens), fitness (esportes de resistência), grau de fadiga, tabagismo. Uma variante ideal abstrata é um homem de 20-30 anos de idade, que estava envolvido no esqui cross-country, com um pequeno histórico de tabagismo.

























